Compressed Air Quality Testing – ISO 8573-1:2010

When compressed air quality testing is conducted, three main contaminants are typically found; water, particles and oil. Contaminants originate from three general sources:
- Contaminants in the surrounding area of the compressor are drawn into the air system through the intake of the air compressor. Ingested contaminants appear in the form of water vapor, hydrocarbon vapours, natural particles and airborne particulates.
- As result of the mechanical compression process, additional impurities may be introduced into the air system. Generated contaminants include compressor lubricant, wear particles and vaporized lubricant.
- A compressed air system will contain in-built contamination. Piping distribution and air storage tanks, more prevalent in older systems, will have contaminant in the form of rust, pipe scale, mineral deposits and bacteria.
What is ISO 8573-1:2010
ISO 8573-1:2010 specifies purity classes of compressed air with respect to particles, water and oil independent of the location in the compressed air system at which the air is specified or measured.
ISO 8573-1:2010 provides general information about contaminants in compressed-air systems as well as links to the other parts of ISO 8573, either for the measurement of compressed air purity or the specification of compressed-air purity requirements.
In addition to the above-mentioned contaminants of particles, water and oil, ISO 8573-1:2010 also identifies gaseous and microbiological contaminants.
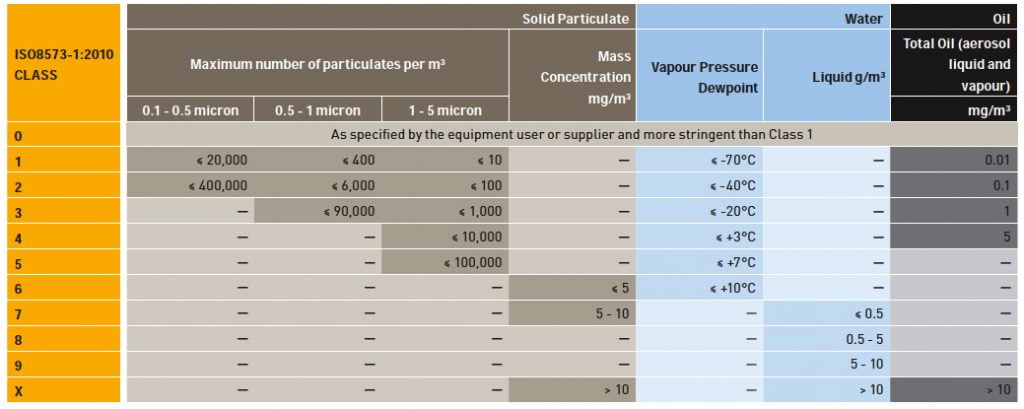
How to designate purity classes
The designation of ISO 8573 Purity Classes includes the following information in the given order: Compressed air purity classes ISO 8573-1:2010 P:W:O where:
P is the purity class for particles (Classes 1 – 7, X)
W is the purity class for water (Classes 1 – 9, X)
O is the purity class for oil (Classes 1 – 4, X)
For example: ISO 8573-1:2010 [2:2:1] indicates Class 2 for particles, Class 2 for water, and Class 1 for oil.
When a class for any particular contaminant P, W, O is not specified, the designation shall be replaced by a hyphen, for example:
[2: – :1] indicates that water will not be tested.
ISO 8573-6 provides test methods for gaseous contaminants and lists the gases of interest: carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), sulphur dioxide (SO2), hydrocarbons (HC), and nitrogen oxides (NOx).
ISO 8573-7 provides test methods for viable microbiological contaminants.



